To cite this section of the Cancer Epigenetics Drug Database
Reference: A. Neudolt, I. Hübscher and I.M. Bennani-Baiti. Lysine demethylase inhibitors. Cancer Epigenetics Drug Database (CEDD) – Experimental dataset, Cancer Epigenetics Society (https://ces.b2sg.org/cedd/experimental_kdmi/), 2016.
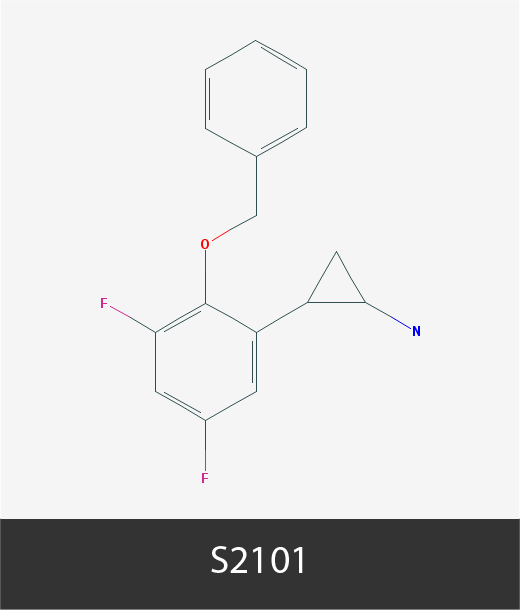
Chemical structures of cancer epigenetic drugs
Brief description of cancer epigenetic drugs
Functional assays used to assess the activity of cancer epigenetic drugs
A word about the Cancer Epigenetics Drug Database – KDMi section
Welcome to the Cancer Epigenetics Drug Database – Experimental dataset for (histone) lysine demethylase inhibitors (KDMi). The epigenetics drug database gives an overview of cancer cell lines sensitivity to KDMi in various functional assays (see assays abbreviations below). The page starts off with the chemical structures of the epigenetic drugs, a succinct description of the epigenetic drugs and functional assays used to test them in cancer cell lines, followed by Tables summarizing the data. Some of the epigenetic drugs also have clinical activities which are summarized in this page. Please note that the epigenetic drug solubility values provided here are only to be used as a guide, and that solubility depends on several variables such as the purity of the solute and solvent used, as well as the temperature used. Similarly, the IC50 values provided herein can be highly dependent on the type of functional assay used and length of incubation of cells with the epigenetic drugs.
The Cancer Epigenetics Drug Database is a work in progress and we rely on our members and readers to bring to our attention data that ought to be included here. We, therefore, welcome any information that you may provide that would help us make this database as useful a tool for your research as possible. You may email us your suggestions at info@ces.b2sg.org, Subject line: CEDD – KDMi, Experimental dataset. The Cancer Epigenetics Drug Database is periodically updated, so please check it again for new data that may be relevant to your research.
Notes:
Lysine demethylase inhibitor (KDMi) activities in cancer cells
| Cell line | IC50 (µM) | Inc1 | Assay2 | ID # |
| 5637 | 0.15 | 3 | MTT | |
| 639-V | 0.38 | 3 | MTT | |
| DLD1 | ~ 0.7 | 3 | MTT | |
| HBLAK | 0.38 | 3 | MTT | |
| HCT116 | ~ 5 | 3 | MTT | |
| HCT-15 | > 4 | 3 | MTT | |
| HEK-293 | 0.2 | 3 | MTT | |
| Hep3B | > 5 | 3 | MTT | |
| HepG2 | 1 – 5 | 3 | MTT | |
| HepG2 | 1 – 3 | 3 | TBE | |
| HepG2 | ~ 1 | 10 | CFA | |
| HepG2 | > 25 | 2 | TTI | |
| HepG2 | 1 – 5 | 0.5 | MMP | |
| HL-7702 | > 25 | 3 | MTT | |
| HT-29 | ~ 7 | 2 | MTT | |
| HT-29 | ~ 3 | 3 | MTT | |
| HT-29 | 0.1 – 1 | 3 | TBE | |
| HT-29 | ~ 1 | 10 | CFA | |
| RT-112 | 0.4 | 3 | MTT | |
| SMMC-7721 | < 5 | 3 | MTT | |
| SW1710 | 0.47 | 3 | MTT | |
| T24 | 0.36 | 3 | MTT | |
| TERT-NHUC | 0.27 | 3 | MTT | |
| UM-UC-3 | 0.51 | 3 | MTT | |
| UM-UC-3 | < 0.5 | 2 | LDH | |
| VM-CUB1 | 0.38 | 3 | MTT | |
| VM-CUB1 | ~ 0.5 – 2.5 | 2 | LDH | |
| VM-CUB1 | < 0.5 | 2 | GLO |
© CEDD, Cancer Epigenetics Society & B² Scientific Group, Ltd. All rights reserved, 2016. Data may be included in academic publications contingent on the citation of the reference on top of this page.
| Cell Line | IC50 (µM) | Inc1 | Assay2 | ID # |
| MM.1S | > 50 | 7 | RCA | |
| MM.1S | > 50 | 7 | A5A |
© CEDD, Cancer Epigenetics Society & B² Scientific Group, Ltd. All rights reserved, 2016. Data may be included in academic publications contingent on the citation of the reference on top of this page.
| Cell line | IC50 (µM) | Inc1 | Assay2 | Additional information3 | ID# |
| CCRF-CEM | ~ 2 | 3 | A5A | ||
| CUTLL1 | ~ 2 | 5 | A5A | ||
| P12-Ichikawa | ~ 2 | 3 | A5A | ||
| SF7761 | ~ 1.5 | 3 | GLO | ||
| SU-DIPG-IV | ~ 6.5 | 3 | GLO | ||
| SU-DIPG-VI | ~ 5 | 3 | GLO | ||
| SU-DIPG-XIII | ~ 3 | 3 | GLO | ||
| THP1 | > 2 | 3 | A5A |
© CEDD, Cancer Epigenetics Society & B² Scientific Group, Ltd. All rights reserved, 2016. Data may be included in academic publications contingent on the citation of the reference on top of this page.
| Cell Line | IC50 (µM) | Inc1 | Assay2 | ID # |
| MM.1S | ~ 20 | 7 | RCA | |
| MM.1S | > 50 | 7 | A5A |
© CEDD, Cancer Epigenetics Society & B² Scientific Group, Ltd. All rights reserved, 2016. Data may be included in academic publications contingent on the citation of the reference on top of this page.
| Cell Line | IC50 (mM) | Inc1 | Assay2 | Additional information3 | ID # |
| A2780 | ~ 4 | 2 | MTS | ||
| A2780cis | ~ 5 | 2 | MTS | Cisplatin-resistant cell line | |
| A549 | ~ 3 | 1 | MTS | ||
| A549 | 3-4 | 2 | MTS | ||
| HEK293T | ~ 4 | 1 | MTS | ||
| HEK293T | ~ 3 | 2 | MTS | ||
| HT-1376 | 1 – 3 | 2 | ACC | ||
| J82 | 1 – 3 | 2 | ACC | ||
| LNCap | < 3 | 2 | TWA | Migration propensity tested | |
| LNCap | ~ 3 | 2 | TWA | Invasion propensity tested | |
| MCF7 | ~ 4 | 2 | MTS | ||
| MCF7 | > 0.25 | 8 | HDA | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | 2.5 – 5 | 2 | MTT | ↑ global H3K4me1&2, H3ac | |
| MDA-MB-231 | >> 0.25 | 10 | HDA | ||
| MDA-MB-468 | 2.5 – 5 | 2 | MTT | ||
| NCI-H460 | ~ 3 | 1 | MTT | ||
| NCI-H460 | 3 – 4 | 2 | MTS | ||
| OVCAR-3 | ~ 3 | 2 | MTS | ||
| SCaBER | ~ 3 | 2 | ACC | ||
| SK-OV-3 | ~ 3 | 2 | MTS | ||
| TCCSUP | 1 – 3 | 2 | ACC |
© CEDD, Cancer Epigenetics Society & B² Scientific Group, Ltd. All rights reserved, 2016. Data may be included in academic publications contingent on the citation of the reference on top of this page.
| Cell Line | IC50 (µM) | Inc1 | Assay2 | Additional information3 | ID # |
| A2780 | 100 – 200 | 2 | MTS | ||
| A2780cis | 100 – 200 | 2 | MTS | Cisplatin-resistant cell line | |
| MCF7 | ~ 100 | 2 | MTS | ||
| OVCAR-3 | ~ 100 | 2 | MTS | ||
| SK-OV-3 | ~ 100 | 2 | MTS |
© CEDD, Cancer Epigenetics Society & B² Scientific Group, Ltd. All rights reserved, 2016. Data may be included in academic publications contingent on the citation of the reference on top of this page.
| Cell Line | IC50 (µM) | Inc1 | Assay2 | Additional information3 | ID # |
| A2780 | ~ 200 | 2 | MTS | ||
| A2780cis | ~ 200 | 2 | MTS | Cisplatin-resistant cell line | |
| MCF7 | 100 – 200 | 2 | MTS | ||
| MOLM-13 | 4.11 | 7 | GLO | ||
| MV4-11 | 6.32 | 7 | GLO | ||
| OVCAR-3 | 100 – 200 | 2 | MTS | ||
| SKM-1 | 10.47 | 7 | GLO | ||
| SK-OV-3 | 100 – 200 | 2 | MTS |
© CEDD, Cancer Epigenetics Society & B² Scientific Group, Ltd. All rights reserved, 2016. Data may be included in academic publications contingent on the citation of the reference on top of this page.
| Cell line | IC50 (mM) | Inc1 | Assay2 | Additional information3 | ID # |
| A2780 | ~ 3 | 2 | MTS | ||
| A2780cis | ~ 3 | 2 | MTS | Cisplatin-resistant cell line | |
| A549 | > 0.02 | 4 | MTS | ||
| A549 | > 0.02 | 4 | A5A | ||
| CME-1 | ~ 1.5 | 2 | MTT | ↑ global H3K4me2 | |
| Fuji | ~ 1.9 | 2 | MTT | ||
| HAT-1376 | ~ 1 | 2 | ACC | ||
| HCC1143 | > 0.25 | 10 | HDA | ||
| HCC1937 | > 0.25 | 10 | HDA | ||
| HS-SY-II | ~ 0.63 | 2 | MTT | ||
| HT-1376 | ~ 1 | 2 | ACC | ||
| HT60 | > 0.05 | 1 | NRM | ||
| HTB-1 | ~ 1-3 | 2 | ACC | ||
| HTB-3 | ~ 1 | 2 | ACC | ||
| HTB-5 | ~ 1-3 | 2 | ACC | ↓ NEP | |
| KYSE-450 | < 0.05 | 2 | WHA | ↓ global H3K4me1 | |
| KYSE-450 | < 0.05 | 2 | TWA | ↓ global H3K4me1 | |
| LN-18 | > 1 | 3 | PIA | ||
| MCF7 | ~ 2 | 2 | MTS | ||
| MCF7 | ~ 0.25 | 6 | HDA | ↑ global H3K4me2; H3K9me2 unchanged | |
| MCF7 | < 0.25 | 8 | HDA | ↑ global H3K4me2; H3K9me2 unchanged | |
| MDA-MB-231 | ~ 0.58 | 5 | CVA | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | > 0.25 | 6 | HDA | ↑ global H3K4me2 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | ~ 0.25 | 8 | HDA | ↑ global H3K4me2 | |
| MGC-803 | ~ 0.1 | 2 | TWA | Migration propensity tested | |
| MGC-803 | ~ 0.1 | 2 | TWA | Invasion propensity tested | |
| MOLM-13 | 0.007 | 7 | GLO | ||
| MV4-11 | 0.002 | 7 | GLO | ||
| OVCAR-3 | ~ 4 | 2 | MTS | ||
| PC-9 | ~ 0.02 | 4 | MTS | ||
| PC-9 | > 0.02 | 4 | A5A | ||
| SKM-1 | 0.001 | 7 | GLO | ||
| SK-OV-3 | ~ 0.94 | 2 | MTT | ↑ global H3K4me2 & PARP1 | |
| SYO-1 | ~ 0.94 | 2 | MTT | ||
| U87 | ~ 1 | 3 | PIA |
© CEDD, Cancer Epigenetics Society & B² Scientific Group, Ltd. All rights reserved, 2016. Data may be included in academic publications contingent on the citation of the reference on top of this page.
| Cell line | IC50 µM | Inc1 | Assay2 | Additional information3 | ID # |
| BT-474 | > 100 | 7 | CFA | ||
| HeLa | ~ 100 | 3 | WST-1 | ↑ H3K4me3 | |
| HeLa | < 50 | 12 | CFA | ↑ H3K4me3 | |
| MCF 10A | > 100 | 5 | WST-1 | ||
| MCF7 | > 100 | 3 | WST-1 | ||
| MCF7 | > 100 | 12 | CFA | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | > 100 | 5 | WST-1 | ||
| PC-9 | > 100 | 7 | CFA | ||
| ZR-75-1 | ~ 100 | 5 | WST-1 |
© CEDD, Cancer Epigenetics Society & B² Scientific Group, Ltd. All rights reserved, 2016. Data may be included in academic publications contingent on the citation of the reference on top of this page.